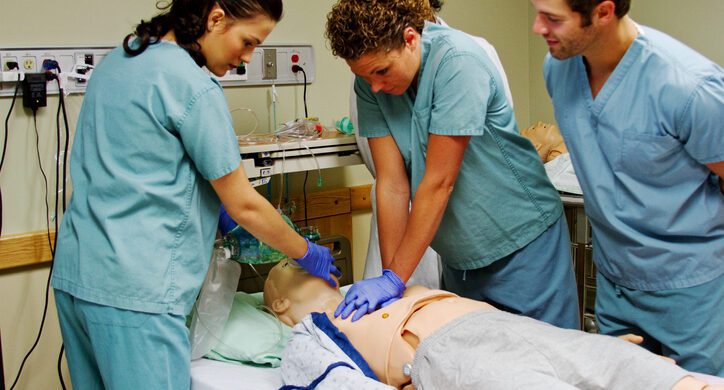
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is an invaluable skill in healthcare, and nurses, as frontline caregivers, play a pivotal role in administering this life-saving technique. CPR is the immediate response to cardiac or respiratory arrest, and the actions taken during those critical moments can make a profound difference in a patient’s outcome. In this article, we will delve into the importance of nurse CPR training, its role in patient care, and how it contributes to a comprehensive approach to healthcare.
Immediate Response to Cardiac Emergencies:
Nurses are often the first healthcare professionals on the scene when a patient experiences cardiac arrest. CPR training equips them with the ability to provide immediate and effective chest compressions and rescue breaths, ensuring that vital oxygen continues to circulate to the brain and other organs during those critical moments before advanced medical assistance arrives.
- Benefits:
- Increased chances of survival, minimized potential long-term effects, and a swift response to cardiac emergencies.
- Considerations:
- Regular CPR training updates ensure that nurses stay current with the latest protocols and techniques.
Enhanced Patient Survival Rates:
Cardiac arrest is a medical emergency that demands prompt action. When nurses are trained in CPR, they significantly contribute to enhancing patient survival rates. By initiating CPR promptly, nurses buy valuable time for the patient, maintaining blood circulation and oxygenation until advanced life support measures can be administered.
- Benefits:
- Improved patient survival rates, increased chances of successful resuscitation, and positive patient outcomes.
- Considerations:
- CPR training includes not only chest compressions and rescue breaths but also the ability to use automated external defibrillators (AEDs) when available.
Skillful Management of Respiratory Arrest:
CPR training goes beyond cardiac arrest scenarios; it also includes the management of respiratory arrest. Nurses trained in CPR can intervene effectively when a patient experiences a sudden cessation of breathing, addressing the root cause and providing the necessary support until normal breathing is restored.
- Benefits:
- Immediate response to respiratory emergencies, prevention of hypoxia, and skillful management of breathing difficulties.
- Considerations:
- Training programs cover techniques for assessing breathing, providing rescue breaths, and addressing airway obstructions.
Ensuring Brain Oxygenation:
Adequate oxygenation is crucial for the brain’s function, and CPR plays a vital role in maintaining this oxygen supply during emergencies. Nurses, by administering effective chest compressions and rescue breaths, ensure that oxygen is circulated to the brain, preventing irreversible damage and increasing the likelihood of a positive neurological outcome.
- Benefits:
- Prevention of brain damage, increased chances of neurologically intact survival, and improved overall patient prognosis.
- Considerations:
- Nurses are trained to prioritize high-quality chest compressions, as effective circulation is fundamental to oxygen delivery.
Integration with Advanced Cardiovascular Care:
CPR is an integral component of advanced cardiovascular care. Nurses, through their CPR training, seamlessly integrate with advanced life support measures provided by emergency medical services and other healthcare professionals. This collaboration ensures a continuum of care for the patient, optimizing their chances of recovery.
- Benefits:
- Seamless integration with advanced cardiovascular care, improved coordination among healthcare providers, and a comprehensive approach to patient resuscitation.
- Considerations:
- Regular simulations and interdisciplinary training enhance communication and coordination during emergency situations.
Nursing Competency and Professional Development:
CPR training is a fundamental aspect of nursing competency, and it forms part of the ongoing professional development for nurses. Maintaining CPR certification ensures that nurses remain adept at providing life-saving interventions, reinforcing their role as competent and skilled healthcare professionals.
- Benefits:
- Demonstrated nursing competency, ongoing professional development, and a commitment to patient safety.
- Considerations:
- Many healthcare institutions require nurses to undergo regular CPR training and maintain current certifications.
Patient and Family Education:
Nurses trained in CPR can extend their knowledge to patient education. By educating patients and their families on the importance of recognizing signs of cardiac or respiratory distress and the steps to take in an emergency, nurses empower them to be proactive partners in their own healthcare and the healthcare of their loved ones.
- Benefits:
- Increased community awareness of cardiac emergencies, proactive patient and family involvement, and a culture of preparedness.
- Considerations:
- Patient education includes recognizing symptoms, calling for help, and initiating basic CPR measures until professional assistance arrives.
Incorporation of Team-Based Approaches:
CPR often involves a team-based approach in healthcare settings. Nurses trained in CPR contribute to the effective functioning of resuscitation teams, collaborating with other healthcare professionals to ensure coordinated and timely interventions. This team-based approach optimizes the chances of successful resuscitation.
- Benefits:
- Improved teamwork, enhanced communication during emergencies, and a cohesive approach to patient care.
- Considerations:
- Regular drills and simulations enhance team coordination and responsiveness during resuscitation efforts.
Supporting a Culture of Safety:
CPR training is integral to supporting a culture of safety within healthcare institutions. Nurses, as key members of the healthcare team, contribute to the development and implementation of safety protocols, including those related to emergency response and resuscitation. This culture of safety extends beyond cardiac emergencies to encompass various aspects of patient care.
- Benefits:
- A culture of safety, proactive risk management, and an emphasis on continuous improvement in patient care.
- Considerations:
- Nurses play a role in safety committees, participate in quality improvement initiatives, and contribute to the development of standardized protocols.
Addressing Ethical Considerations:
Ethical considerations are paramount in healthcare, especially during emergency situations. Nurses trained in CPR navigate these ethical considerations, ensuring that decisions made during resuscitation efforts align with the patient’s wishes, advance directives, and the principles of beneficence and non-maleficence.
- Benefits:
- Ethical decision-making during emergencies, respect for patient autonomy, and adherence to ethical guidelines.
- Considerations:
- Training includes discussions on ethical dilemmas, communication with patients and families, and respecting end-of-life preferences.
Community Outreach and Public Health Initiatives:
CPR-trained nurses can extend their expertise to community outreach and public health initiatives. Participating in educational programs, conducting CPR workshops, and raising awareness about the importance of CPR in the community contribute to a broader public health effort.
- Benefits:
- Increased community resilience, improved public awareness of CPR, and a potential increase in bystander-initiated CPR.
- Considerations:
- Nurses can collaborate with community organizations, schools, and local healthcare agencies to promote CPR education and training.
Nurse CPR training is a cornerstone of patient care, emphasizing the immediate response to cardiac and respiratory emergencies. Nurses, through their CPR skills, contribute to increased patient survival rates, seamless integration with advanced cardiovascular care, and a culture of safety within healthcare institutions. Beyond the clinical setting, nurse CPR training extends to patient and family education, community outreach, and ethical considerations, reflecting the holistic nature of nursing care. As frontline caregivers, nurses play an indispensable role in shaping positive patient outcomes, and CPR training equips them with the tools to make a difference in those critical moments when every second counts.
Y-CPR Academy provides American Heart Association (AHA) CPR training classes with professional, certified AHA instructors who specialize in nurse CPR training, CPR training for workplaces, CPR training for healthcare providers, CPR training for childcare providers, and CPR training for individuals and groups. Contact Y-CPR Academy today to learn more and ask about our mobile classes.